
HUMAN IDENTIFICATION
Craniofacial Superimposition
PRODUCT
This software enables fully automated skull-face overlays within seconds. It supports overlays using one or multiple photos of candidates alongside a 3D model of the skull. The tool assists forensic experts in conducting fast, precise, and objective comparisons, whether in 1-to-1 or 1-to-n candidate scenarios. The results of the superimposition are quantified using a likelihood ratio, while the software also guides experts to draw accurate and repeatable conclusions.

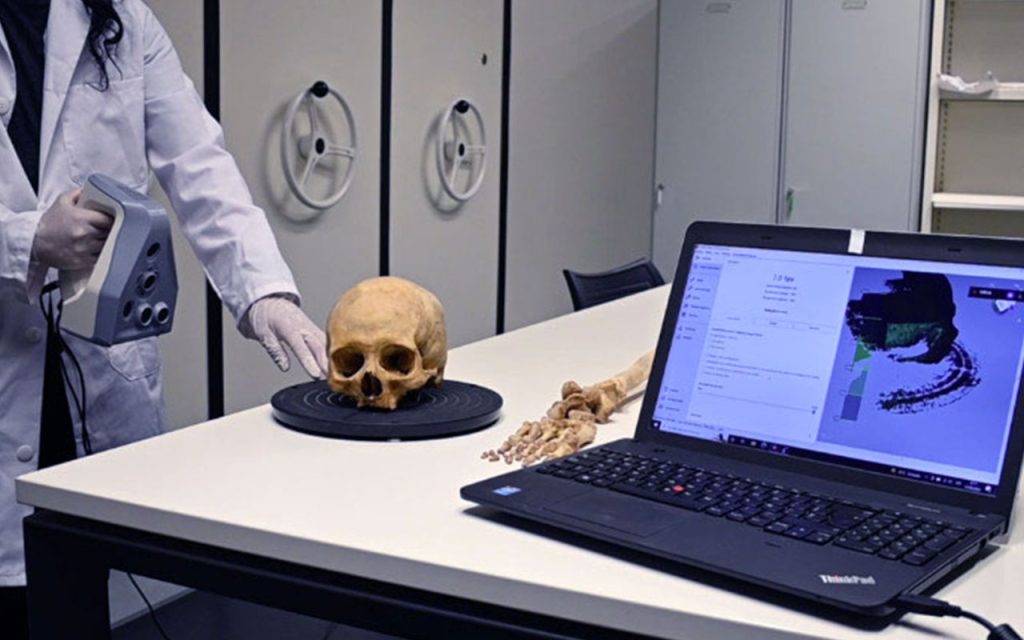
Scan: The module utilizes a 3D model of the unidentified individual’s skull and one or more facial images of missing persons for comparison. These 3D models can be obtained through medical image segmentation, 3D scanners, or photogrammetry systems.
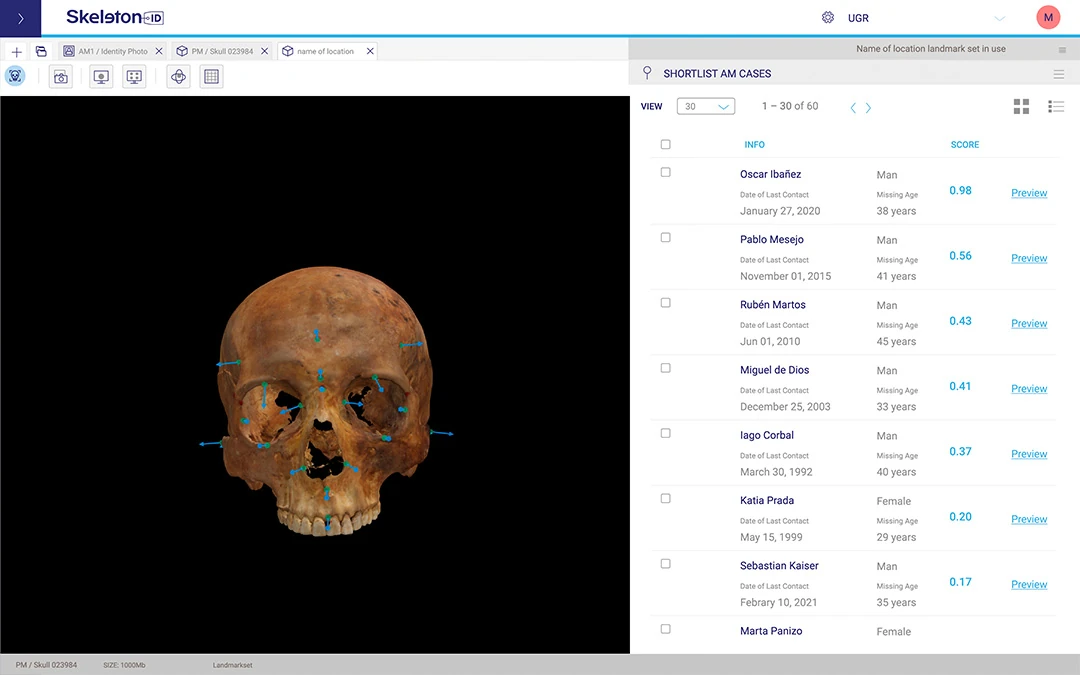
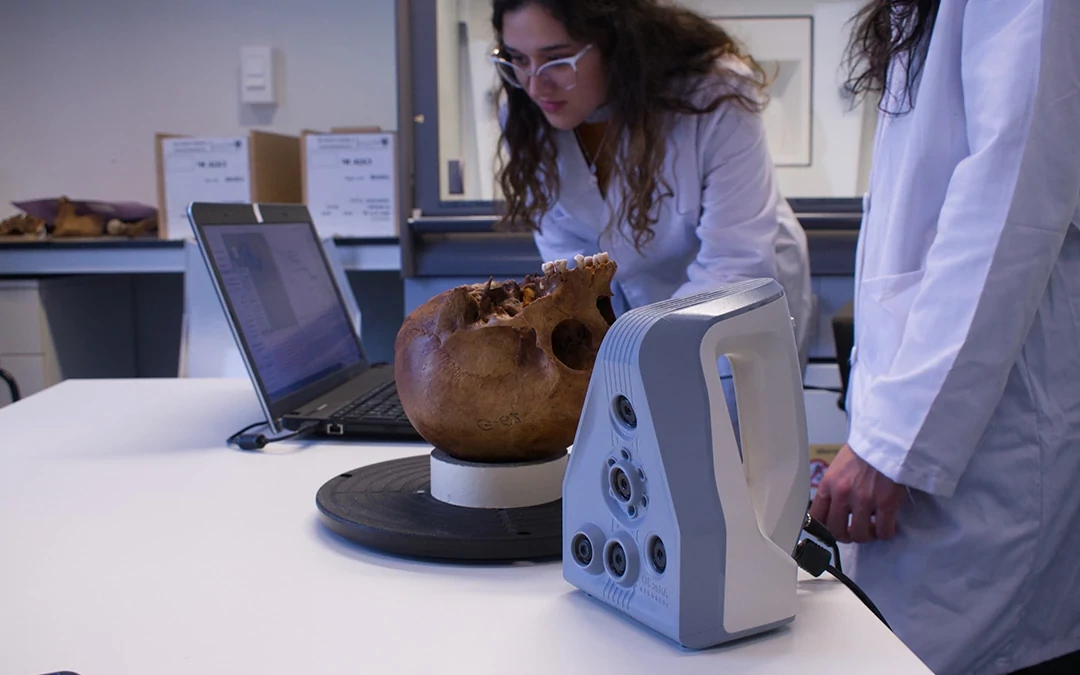
Comparison: Antemortem data may include one or multiple photos of potential candidates or entire databases.
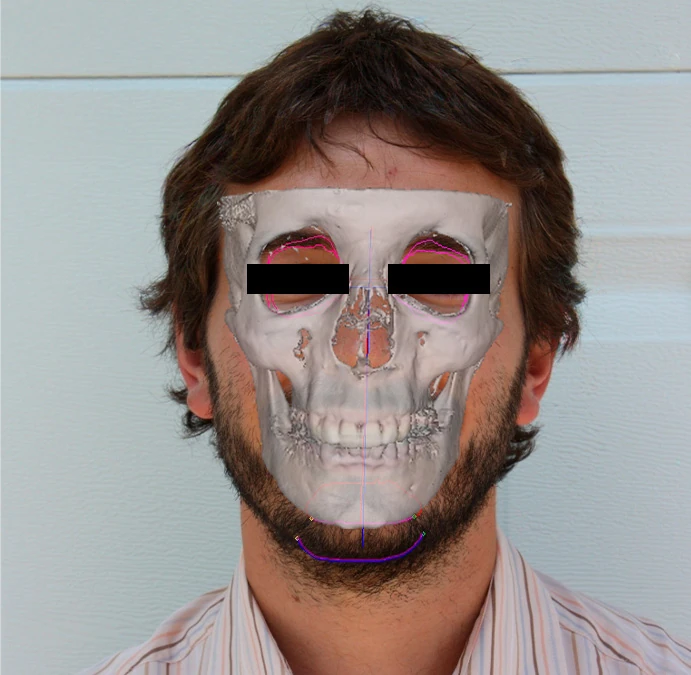
Superimposition: The software performs fully automated 2D/3D craniofacial superimposition, enhanced by Artificial Intelligence.
Ranking: AI generates a ranking of potential candidates, prioritizing the most likely matches. Experts can then focus on reviewing the top-ranked candidates.
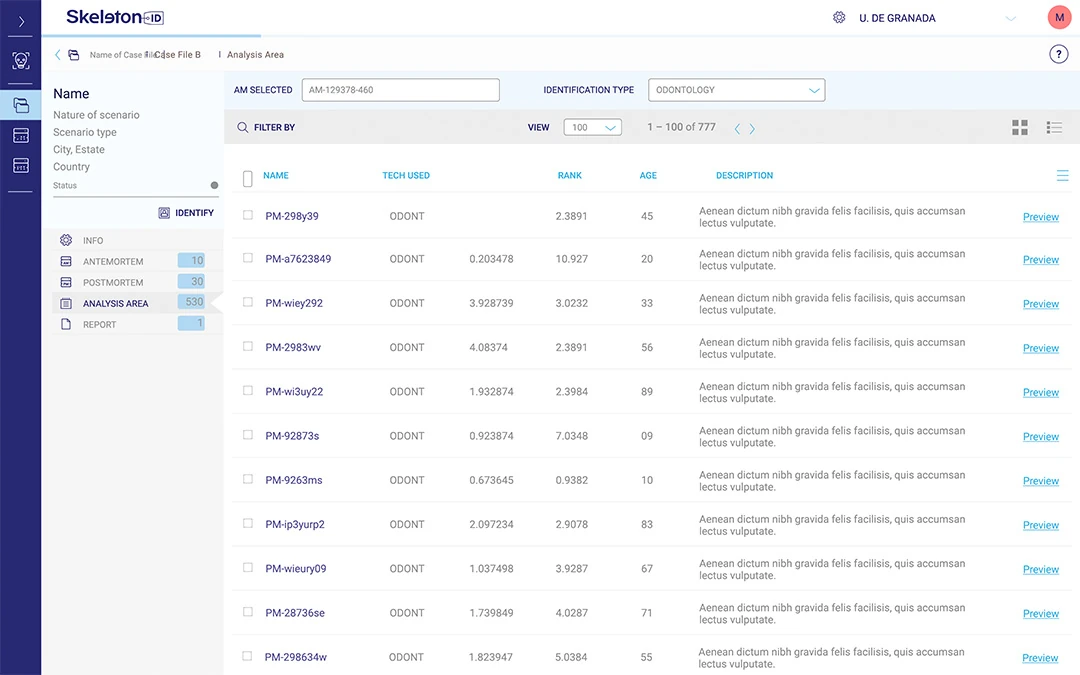
Ranking: AI generates a ranking of potential candidates, prioritizing the most likely matches. Experts can then focus on reviewing the top-ranked candidates.
At Panacea, we conducted two international validation studies of the Skeletal Comparison Framework (SCF) in accordance with MEPROCS guidelines. These studies assessed the reliability of AI-based methods and provided the scientific community with a replicable validation framework. The research encompassed an unprecedented number of cases, exceeding thousands of comparisons.
VIDEOS
OTHER REFERENCES
- A quick Introduction to Soft Tissue Studies
- A quick introduction to Craniofacial Superimposition
- Automatic landmark location on human skulls
- Posest-SFO: automatic skull-face overlay
- Understanding camera parameters
- Computer-aided craniofacial superimposition validation study: the identification of the leaders and participants of the Polish-Lithuanian January Uprising (1863-1864)
- A Robust and Efficient Method for Skull-Face Overlay in Computerized Craniofacial Superimposition
SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS
P. Martínez-Moreno, A. Valsecchi, P. Mesejo, O. Ibáñez, S. Damas. Evidence Evaluation in Craniofacial Superimposition using Likelihood Ratio. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 18 (9). Submitted in 2023.
A Valsecchi, S Damas, O Cordón. A Robust and Efficient Method for Skull-Face Overlay in Computerized Craniofacial Superimposition. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 13:8 (2018), 1960-1974. Impact factor 2018: X.X. Computer Science, Theory & Methods. Order: 10/105. D1. Q1
C. Campomanes-Álvarez, R. Martos-Fernández, C. Wilkinson, O. Ibáñez, and O. Cordón. Modeling skull-face anatomical/morphological correspondence for craniofacial superimposition-based identification. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 13:6 (2018) 1481 – 1494. DOI 10.1109/TIFS.2018.2791434. Impact
factor 2018: 6.211. Computer Science, Theory & Methods. Order: 5/104. D1. Q1.
C. Campomanes-Álvarez, O. Ibáñez, O. Cordón, C. Wilkinson. Hierarchical Decision Support Framework for Craniofacial Superimposition. Information Fusion 39 (2018), 25-40. Impact factor 2018: 10.716. Category: Computer Science, Theory & Methods. Order: 2/104. D1. Q1.
E. Bermejo, S. Damas, C. Campomanes-Alvarez, A. Valsecchi, O. Ibañez. Genetic algorithms for skull-face overlay including mandible articulation. Information Sciences 420 (2017) 200-217. Impact factor 2017: 4.305. Category: Computer Science, Theory & Methods. Order: 12/148. D1. Q1.
O. Ibáñez, R. Vicente, D. Navega, B. R. Campomanes-Álvarez, C. Cattaneo, R. Jankauskas, M. I. Huete, F. Navarro, R. Hardiman, E. Ruiz, K. Imaizumi, F. Cavalli, E. Veselovskaya, D. Humpire, J. Cardoso, F. Collini, D. Mazzarelli, D. Gibelli, S. Damas. MEPROCS framework for Craniofacial Superimposition: validation study. Legal Medicine 23 (2016) 99-108. DOI 10.1016/j.legalmed.2016.10.007. Impact factor 2016: 1.276. Category: MEDICINE, LEGAL. Order: 7/15. Q2.
O. Ibáñez, A. Valsecchi, F. Cavalli, M.I. Huete, B.R. Campomanes-Alvarez, C. Campomanes-Alvarez, R. Vicente, D.S. Navega, A. Ross, C. Wilkinson, R. Jankauskas, K. Imaizumi, R. Hardiman, P.T. Jayaprakash, E. Ruiz, F. Molinero, P. Lestón, E. Veselovskaya, A. Abramov, M. Steyn, J. Cardoso, D. Humpire, L. Lusnig, D.M. Gibelli, D. Mazzarelli, D. Gaudio, F. Collini, S. Damas. Study on the criteria for assessing skull-face correspondence in craniofacial superimposition. Legal Medicine 23 (2016) 59-70. Impact factor 2016: 1.276. Category: MEDICINE, LEGAL. Order: 7/15. Q2.
C. Campomanes-Álvarez, O. Ibáñez, O. Cordón. Design of Criteria to Assess Craniofacial Correspondence in Forensic Identification based on Computer Vision and Fuzzy Integrals. Applied Soft Computing 46 (2016) 596-612. Impact factor 2016: 3.541. Category: COMPUTER SCIENCE, ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE. Order: 21/133. Q1.
O. Ibáñez, R. Vicente, D.S. Navega, C. Wilkinson, P.T. Jayaprakash, M.I. Huete, T. Briers, R. Hardiman, F. Navarro, E. Ruiz, F. Cavalli, K. Imaizumi, R. Jankauskas, E. Veselovskaya, A. Abramov, P. Lestón, F. Molinero, J. Cardoso, A.S. Çağdir, D. Humpire, Y. Nakanishi, A. Zeuner, A.H. Ross, D. Gaudio, S. Damas. Study on the performance of different
craniofacial superimposition approaches (I). Forensic Science International, 257 (2015) 496-503. Impact factor 2015: 1.950. Category: MEDICINE, LEGAL. Order: 5/15.Q2.
S. Damas, C. Wilkinson, T. Kahana, E. Veselovskaya, A. Abramov, R. Jankauskas, P.T. Jayaprakash, E. Ruiz, F. Navarro, M.I. Huete, E. Cunha, F. Cavalli, J. Clement, P. Leston, F. Molinero, T. Briers, F. Viegas, K. Imaizumi, D. Humpire, O. Ibáñez. Study on the performance of different craniofacial superimposition approaches (ii): best practices
proposal. Forensic Science International, 257 (2015) 504-8. Impact factor 2015: 1.950. Category: MEDICINE, LEGAL. Order: 5/15. Q2.
M.I. Huete, T. Kahana, O. Ibáñez, C. Wilkinson. Past, present, and future of Craniofacial Superimposition: literature and international surveys. Legal Medicine 17:4 (2015) 267-278. Impact factor 2015: 1.442. Category: MEDICINE, LEGAL. Order: 8/15. Q3.
B.R. Campomanes -Álvarez, O. Ibáñez, C. Campomanes-Álvarez, S. Damas, O. Cordón. Modeling facial soft tissue thickness for automatic skull-face overlay. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Security 10:10 (2015) 2057-2070. Impact factor 2015: 2.441. Computer Science, Theory & Methods. Order: 10/105. D1. Q1.
O. Ibáñez, F. Cavalli, B. R. Campomanes-Alvarez, C. Campomanes-Álvarez, A. Valsecchi, M. I. Huete. Ground truth data generation for skull-face overlay. International Journal of Legal Medicine 129:3 (2015) 569–581. Impact factor 2015: 2.862. MEDICINE, LEGAL. Order: 2/15. D1. Q1.
B. R. Campomanes-Álvarez, O. Ibáñez, F. Navarro, I. Alemán, M. Botella, S. Damas, O. Cordón. Computer Vision and Soft Computing for Automatic Skull-Face Overlay in Craniofacial Superimposition. Forensic Science International 245 (2014) 77-86. Impact factor 2014:2.140. MEDICINE, LEGAL. Order: 3/15. Q1.
O. Ibáñez, O. Cordón, S. Damas, J. Santamaría. An advanced scatter search design for skull-face overlay in craniofacial superimposition. Expert Systems with Applications 39:1 (2012) 1459-1473. Impact factor: 1.854. Category: OPERATIONS RESEARCH & MANAGEMENT SCIENCE. Order: 13/78. Q1.
O. Ibáñez, O. Cordón, S. Damas. A cooperative coevolutionary approach dealing with the skull–face overlay uncertainty in forensic identification by craniofacial superimposition. Soft Computing 16:5 (2012) 797-808. Impact factor: 1.124. Category: COMPUTER SCIENCE, ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE. Order: 63/114. Q3.
S. Damas, O. Cordón, O. Ibáñez, J. Santamaría, I. Alemán, MC. Botella, F. Navarro. Forensic Identification by Computer-aided Craniofacial Superimposition: A Survey. ACM Computing Surveys 43:4 (2011) 27:1-27:27. Impact factor: 4.529. Category: COMPUTER SCIENCE, THEORY & METHODS. Order: 1/99. D1. Q1.
O. Ibáñez, O. Cordón, S. Damas, J. Santamaría. Modeling the skull-face overlay uncertainty using fuzzy sets. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems 19:5 (2011) 946- 959. Impact factor: 4.260. Category: COMPUTER SCIENCE, ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE. Order: 5/111. D1. Q1.
O. Ibáñez, L. Ballerini, O. Cordón, S. Damas, J. Santamaría. An Experimental Study on the Applicability of Evolutionary Algorithms to Craniofacial Superimposition in Forensic Identification. Information Sciences 179:23 (2009) 3998-4028. Impact factor: 3.291. Category: COMPUTER SCIENCE, INFORMATION SYSTEMS. Order: 6/116. D1. Q1.
VALIDATION STUDIES
1. R. Martos, R. Guerra, F. Navarro, M. Peruch, K. Neuwirth, A. Valsecchi, R. Jankauskas, O. Ibáñez. Computer-aided Craniofacial Superimposition validation study: the identification of the leaders and participants of the Polish-Lithuanian January Uprising (1863-64). International Journal of Legal Medicine (2022) DOI: 10.1007/s00414-022-02929-4. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36520206. Order: 5/17. Q2.
2. R. Guerra, R. Martos, O. Ibáñez, A. Valsecchi, E. Bermejo, E. Kimmerle, G. Goad. International validation study of AI-guided Craniofacial Superimposition in an American population sample. Poster at 75th Anniversary Conference of the American Academy of Forensic Sciences. 13-18 February 2023, Orlando, Florida.
3. Ibáñez, Ó., Bermejo, E. & Valsecchi, A. Study on the identification limits of craniofacial superimposition. Pre-print at
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2301.09461 2023 Jan 23.