HUMAN IDENTIFICATION
Comparative Radiography
PRODUCT
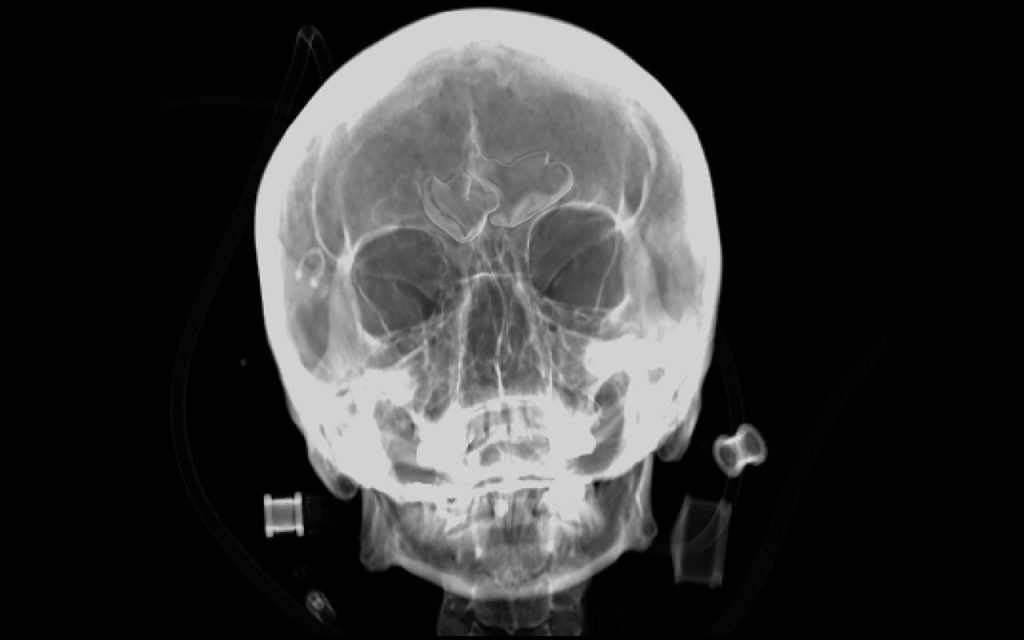
Comparative Radiography (CR) is a forensic identification technique that compares skeletal structures in antemortem and postmortem radiographic images. Forensic literature highlights several skeletal structures as useful for identification or candidate shortlisting due to their individuality and uniqueness.
The most commonly used skeletal structures in CR are found in the skull, chest, and thoracic regions. In the skull, key features include teeth, frontal sinuses, and the cranial vault. In the chest and thoracic regions, the clavicles and vertebral features are most frequently analyzed. Additionally, a few bones outside these areas, such as the hand bones and patella, are traditionally considered.
The software enables automatic comparisons between 3D model segmentations or volumetric images (CBCT/CT) of frontal and sphenoid sinuses for identification purposes.
VIDEOS
OTHER REFERENCES
- A quick introduction to Comparative Radiography
- Deep architectures for the segmentation of frontal sinuses in X-ray images: Towards an automatic forensic identification system in comparative radiography
- Performance analysis of real-coded evolutionary algorithms under a computationally expensive optimization scenario: 3D–2D Comparative Radiography
SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS
O. Gómez, P. Mesejo, O. Ibáñez, A. Valsecchi, E. Bermejo, A. Cerezo, J. Pérez, I. Alemán, T. Kahana, S. Damas, O. Cordón. Artificial Intelligence for Comparative Radiography. Submitted to International Journal of Legal Medicine in 2022.
O.D. Gómez, P. Mesejo, O. Ibáñez, O. Cordón. Deep architectures for the segmentation of frontal sinuses in X-Ray images: towards an automatic forensic identification system in comparative radiography. Neurocomputing,456 (2021), 575-585. Impact factor 2019: 4.438. Category: COMPUTER SCIENCE, ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE.
Order: 28/137. Q1.
O.D. Gómez, O. Ibáñez, A. Valsecchi, E. Bermejo, D. Molina, O. Cordón. Performance analysis of real-coded evolutionary algorithms under a computationally expensive optimization scenario: 3D–2D Comparative Radiography. Applied Soft Computing, 97 (2020), 106793. Impact factor 2019: 5.472. Category: COMPUTER SCIENCE,
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE. Order: 20/136. Q1.
O.D. Gómez, P. Mesejo, O. Ibáñez, A. Valsecchi, O. Cordón Deep architectures for highresolution multi-organ chest X-ray image segmentation. Neural Computing and Applications 32 (2020) 15949–15963. Impact factor 2019: 4.664. Category: COMPUTER SCIENCE, ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE. Order: 21/133. Q1.